|
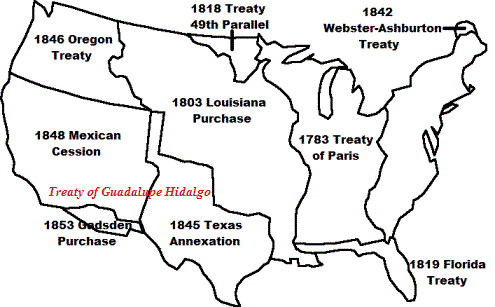
Map
of 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo |
1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo: Summary
The peace Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo ended the
Mexican
American War which was primarily caused by the
refusal of Mexico to acknowledge the independence of Texas and its
admission to the United States, and by border
disputes.
The peace Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo was made in 1848 in which Mexico agreed to abandon
claims to Texas, California, New Mexico, Nevada, Utah and Colorado.
In return the United States agreed to pay Mexico $15,000,000 and
withdraw its armies from Mexican soil. The Mexicans owed American
settlers large sums of money and the provisions of the Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo also agreed to pay the claims of American citizens on
Mexico. These claims proved to amount to $3,500,000.
The United
States therefore paid just $18,500,000 for this massive and
extremely valuable addition to its territory and increased the
popular belief in the
Manifest Destiny
of the United States.
What was the date of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo?
The date the Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo was signed on February 2, 1848.
The
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, was ratified by the U.S.
Senate on March 10th, 1848 and ratified by the Mexican
Congress on May 25th, 1848. As an additional point of interest the informal Treaty of Cahuenga
that ended the fighting of the
Mexican American War in Alta California was signed on January 13, 1848.
Where was the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo signed?
The Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo was signed at Villa de Guadalupe Hidalgo, which is a
northern neighborhood of Mexico City.
Who negotiated the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo?
The Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo was negotiated by Nicholas Trist (1800 - 1894) for the
United States with a special commission representing the collapsed
government of Mexico led by Don Bernardo Couto, Don Miguel de
Atristain, and Don Luis Gonzaga Cuevas.
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo Background History for kids: President Polk
and Nicholas Trist
During the Mexican
American War Nicholas Trist had been sent by President James K. Polk
to arrange an armistice with Mexico for up to $30 million.
California was divided into Alta ("Upper") and Baja ("Lower")
California.
President Polk made it clear that if Trist could not obtain Baja
California and additional territory to the south, then the offer to
the Mexicans should be reduced to $20 million. These original
negotiations failed but Nicholas Trist went on to negotiate the Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo and ignored President Polk's specific instructions.
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo Background History for kids: Nicholas Trist
ignores President Polk
Ignoring the instructions of the president Nicholas Trist negotiated
the Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo and, to the absolute fury of James Polk, drew the boundary
line directly West from Yuma to San Diego instead of from Yuma south
to the Sea of Cortez leaving all of Baja California almost separate
from Mexico. There was not enough time for renegotiation. The Treaty
of Guadalupe Hidalgo had to stand as Nicholas Trist had negotiated
and the president most reluctantly had to give it his
approval.
1848
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo Text
Click the following link to read the full
Text of the
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo.
1848
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo Terms and Provisions
Under the terms of the
treaty negotiated by Nicholas Trist, Mexico ceded Upper California
and New Mexico to the United States. This was known as the
Mexican Cession (see Map below) and included present-day Arizona and
New Mexico and parts of Utah, Nevada, and Colorado. Mexico
relinquished all claims to Texas and recognized the Rio Grande as
the southern boundary with the United States. The Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo Important terms and provisions were as follows:
● The Treaty
of Guadalupe Hidalgo brought an official end to the
Mexican-American War (1846–48)
● Article V
of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo dealt with the Mexican
Cession and included present-day Arizona and New Mexico and
parts of Utah, Nevada, and Colorado. In Article V Mexico
relinquished all claims to Texas and recognized the Rio Grande
as the southern boundary with the United States
● Articles
VIII and IX of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo included
provisions for the protection of property and civil rights of
Mexican nationals living within the new boundaries of the United
States. U.S. citizenship was granted to Mexicans living in the
territory ceded by Mexico to the United States and guaranteed Mexican Americans
"the right to their property, language, and culture."
● Article X of the Treaty of
Guadalupe Hidalgo had guaranteed the protection of Mexican land
grants but
this was deleted on March 10, 1848 by
the US Senate during the ratification process
● Article XI
of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo included the promise of the
United States to police its boundaries
● Article
XII of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo agreed that the United
States would pay Mexico $15,000,000 "in consideration of the
extension acquired by the boundaries of the United States"
● Article XV
of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo agreed to pay American
citizens debts owed to them by the Mexican government
● Article
XXI of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo agreed to the compulsory
arbitration of future disputes between the two countries
1848
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo Significance
The significance of the Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo was:
● Zachary
Taylor was heralded as a national hero during the
Mexican-American War and became a future president of the United
States
● The Treaty
of Guadalupe Hidalgo
added an additional 525,000 square miles to United States
territory, including the land that makes up all, or parts of,
present-day Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico,
Utah and Wyoming
● The
California Gold Rush
started with the discovery of gold by James W. Marshall
at Sutter's Lumber Mill in Coloma on January 24, 1848, before
the treaty was even signed
● Mexico
relinquished all claims to Texas and recognized the Rio Grande
as America’s southern boundary
● The
Gadsden Purchase was agreed in 1853
●
The treaty increased the popular belief in the
Manifest Destiny of the
United States of America
● The
Abolitionist Movement in
the north opposed the annexation of Mexican territory
● The
acquisition of the new lands in the of the Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo ignited the slavery debate which
would lead to the American Civil war (1861-1865)
1848 Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo for kids
The info about the Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo provides interesting facts and
important information about this important event that occured during the presidency of the 11th President of the United States of America.
|

Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo |
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo: Map
The United States Territorial Expansion Map provides an over view of the
treaties made in order to achieve the expansion of the United States. The Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo granted all land from Texas to California, minus
the Gadsden Purchase.
The Gadsden Purchase: The Boundary Line
The Mexican and American
commissioners failed to agree on the boundary line. The
United States therefore paid an additional $10 million to
Mexico and received an additional strip of land between
the Rio Grande and the Colorado rivers giving the United
States its present southern boundary. This agreement was
made in 1853 by James Gadsden for the United States, and
this additional land bought from Mexico is usually
referred to as the
Gadsden Purchase.
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo for kids - President James K Polk Video
The article on the
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo provides an overview of one of the Important issues of his presidential term in office. The following
James K Polk video will
give you additional important facts and dates about the political events experienced by the 11th American President whose presidency spanned from March 4, 1845 to March 4, 1849.
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
●
Facts and summary of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
●
Definition of the
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in US history
●
Facts about the
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
●
James K Polk Presidency from March 4, 1845 to March 4, 1849
●
Fast, fun, facts about the Treaty of
Guadalupe Hidalgo
●
Foreign & Domestic
policies of President James K Polk
● James K Polk
Presidency and the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo for schools, homework, kids and
children
|