|
What were the Causes of the
Mexican American War?
What were the Causes of
the Mexican American War? The causes of the Mexican American
War were:
● The goal of James Polk
for American territorial expansion
● The ideals
of the
Manifest Destiny
● Cultural differences
between the Mexicans and the Americans settlers in the area
● The
refusal of Mexico to acknowledge the independence of Texas and
its admission to the United States
● Border
disputes - Mexico claimed the Nueces River as its northeastern
border, while the U.S. claimed the Rio Grande River
|
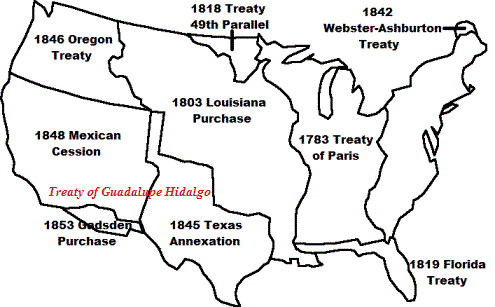
Mexican American
War Map and US Territorial Expansion Map |
The Mexican American War Map
The Mexican American War Map shows an over view of the
territorial expansion of the United States and the 1845
Texas Annexation and the 1848 Mexican cession agreed in
the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. The Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo granted all land from Texas to California, minus
the
Gadsden Purchase.
Mexican American War Map: Manifest Destiny
The Mexican American War Map provides an overview of the
massive areas of dispute between Mexico and the United
States. Mexico never acknowledged the independence of
Texas and protested against its admission to the United
States and disputed the border. Offers were made by the
US to purchase the land but Mexico refused.
President James K. Polk, with his belief in the Manifest
Destiny of the United States (the conviction that
Americans were divinely ordained to expand and dominate
the continent) ordered General Zachary Taylor to march
to the Rio Grande and occupy the disputed territory.
Taylor was attacked by the Mexicans and the United
States declared war on Mexico
The Mexican American War Summary for kids
The summary of the Mexican American War can be divided into three
parts:
● The
seizure of California led by Stephen Kearny (detailed info can
be found in the article on the
Bear Flag Revolt and the California Republic)
● The
Mexican campaign headed by General Zachary Taylor across the Rio Grande
● The
Mexican campaign headed by General Winfield Scott that ended in the
capture of the City of Mexico
The Mexican American War Summary: The General Zachary
Taylor Campaign
The Mexican campaign led by General Zachary Taylor in the Mexican American
War started with his orders from President James Polk The objective
of the Taylor's campaign was to preserve the line of the Rio
Grande and then to advance into Mexico. The May 8, 1846 Battle of
Palo Alto, the Siege of Fort Texas and the May 8, 1846 Battle of
Resaca de la Palma were fought before the actual declaration of war
on May 13, 1846 and resulted in victories for the United States.
These victories achieved Taylor's first goal of maintaining the line
of the Rio Grande. General Taylor crossed the Rio Grande in
September 1846 and outnumbered by the Mexican army, faced a series
of defeats. The General Taylor took his revenge at the Battle of
Buena Vista on February 22-23, 1847. His victory at the Battle of
Buena Vista was the last combat during Zachary Taylor's campaign.
The Mexican American War Summary: The General Winfield
Scott Campaign
The goal of the Mexican campaign led by General Winfield Scott in the
Mexican American War was that he should land at Vera Cruz, march 200
miles to the city of Mexico and capture Mexico city and force the
Mexicans to make peace. Between August-September 1846 U.S.
volunteers assemble under General John E. Wool and join General
Zachary Taylor and his troops. General Winfield Scott, although
still considerably outnumbered, captured Veracruz with the
help of the US navy in the Siege of Veracruz from March 9-29, 1847.
Other victories followed en route to the City of Mexico. On August
20, 1847, the troops of General Scott beat the Mexicans in three
pitched battles, and on September 14, 1847 he entered the city with
his army. The Mexican American War continued with a few minor
battles but the Mexican American War had been won by the United
States and their victory sealed in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
on March 10, 1848.
Mexican American War Timeline and Facts for kids
The Mexican American War Facts and Timeline for kids is
detailed below. The history of the Mexican American War is told in a
factual timeline sequence consisting of a series of short facts
providing a simple method of relating the famous people and events
surrounding the Mexican American War.
Mexican
American War Timeline and Facts for kids
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 1:
1821: The Mexicans won
their independence from Spain and founded the Mexican
Republic. Immigrants from the US settled in Texas and Alta
California
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 2:
April 6, 1830: The
Mexican government bans US immigration
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 3:
October 2, 1835: The
Texas Revolution
began and on March 2, 1835 Texas
declares independence from Mexico
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 4:
March 3, 1837: United
States recognizes the Republic of Texas
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 5:
March 4, 1845: James Polk
becomes US President. His goal is American territorial
expansion to the Pacific coast
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 6:
1845:
John O’Sullivan initiates
the phrase 'Manifest Destiny'
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 7:
1845: President James
Polk offers to purchase the lands but the Mexican
government refuses to sell the land at any price
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 8:
December 29, 1845:
President Polk signs the Joint Resolution admitting
Texas as a state - refer to
Texas Annexation.
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 9:
Mexico refuses to
acknowledge the independence of Texas and its admission
to the United States. Disputes arose regarding the
southern boundary of Texas
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 10:
U.S. forces invade
Mexican territory on two main fronts. U.S. cavalry under
Stephen W. Kearny invades western Mexico, reinforced by
a Pacific fleet under John D. Sloat. Zachary Taylor and
John E. Wool invade the south of Mexico as far as
Monterrey
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 11:
May 8, 1846: U.S.
troops defeat the Mexicans at the Battle of Palo Alto,
the first official battle of the war
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 12:
The Battle of Resaca
de la Palma when Mexican troops attack Fort Texas
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 13:
May 13, 1846:
Congress declares war on Mexico
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 14:
June 14, 1846: The
start of the
Bear Flag
Revolt and the California Republic launched by
American settlers (the Bear Flaggers) against Mexico in
the Mexican territory of Alta California. The Bear Flag
Revolt lasts 25 days
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 15:
June 14, 1846:
William B. Ide is made the first, and only, President of
the California Republic for 25 days
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 16:
June 23, 1846: John
C. Fremont arrives in California with 60 American soldiers
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 17:
July 7, 1846:
John D. Sloat leads the US navy to victory at the Battle
of Monterey and issues a proclamation announcing that
California was now part of the United States.
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 18:
July 9, 1846: William
B. Ide and the other "Bear Flaggers" joined John C.
Fremont and the U.S. armed forces in taking possession
of California from Mexico.
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 19:
July 9, 1846: The
Bear Flag revolt ends due to the California Annexation
by the United States.
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 20:
August 8,1846: The amendment known as the
Wilmot Proviso was
introduced in the US Congress
to the $2million
appropriations Bill to finance the settlement of the
Mexican American War
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 21:
September 20, 1846:
General Zachary Taylor captures the Mexican city of
Monterrey. Between August-September 1846 U.S.
volunteers assemble under General John E. Wool and join
General Taylor and his troops
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 22:
September 25, 1846:
Stephen Kearny sets out for California on with a force
of 300 men to assist in the conquest of California
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 23:
September 22-30,
1846: Mexican Victory at the Siege of Los Angeles
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 24:
September - December
1846: Mexican victories at the Battle of Chino, the
Battle of Dominguez Rancho and the Battle of San Pasqual
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 25:
December 1846:
Antonio Lopez de Santa Anna returns from exile in Cuba,
stages a coup against the government and declares
himself the new President of Mexico
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact
26: January 10, 1847: Stephen Kearny's dragoons, Robert
Stockton's marines, and two companies of John Fremont's
California Battalion win the battles of San Gabriel and
the La Mesa and retake control of Los Angeles
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 27:
February 23, 1847:
The U.S. under General Zachary Taylor wins the Battle of
Buena Vista against General Santa Anna
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 28:
March 9-29, 1847:
American victory at the Siege of Veracruz
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 29:
April 17-18, 1847:
The U.S. wins the Battle of Cerro Gordo under the
leadership of General Winfield Scott
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 30:
July 1847: U.S.
diplomat Nicholas Trist is unsuccessful at reaching an
agreement with Santa Anna and the war continues
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 31:
August-September
1846: U.S. volunteers assemble under General John E.
Wool and join General Taylor and his troops.
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 32:
September 13-15,
1847: American victory at the Siege of Los Angeles
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 33:
September 14, 1847:
The U.S. under General Scott wins the Battle of Mexico
City.
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 34:
January 13, 1848: The
Californio forces in California capitulated to John C.
Fremont and his California Battalion.
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 35:
January 13, 1848: The
informal Treaty of Cahuenga ended the fighting of the
Mexican–American War in Alta California
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 36:
January 24, 1848:
The
California Gold
Rush started with the discovery of gold by
James W. Marshall at Sutter's Lumber Mill in Coloma
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 37:
February 2, 1848: Mexico formally ceded territories to the United
States under the terms of the
1848 Treaty of Guadalupe
Hidalgo
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 38:
March 10, 1848: The
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, is ratified by the U.S.
Senate on March 10th
Mexican American War
Timeline Fact 39:
May 25th, 1848: The
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo is ratified by the
Mexican Congress on May 25th
Mexican
American War Timeline and Facts for kids
Mexican American War
for kids
The info about the Mexican American
War provides interesting facts and
important information about this important event that occured during the presidency of the 11th President of the United States of America.
Mexican American War Battles
The names and dates of
Important Mexican American War
battles were as follows:
Dates of Battles - Names of Battles
- Results of Battles
May 8, 1846 - Battle of Palo Alto
- American Victory
May 8, 1846 - Siege of Fort Texas
- American Victory
May 9, 1846 - Battle of Resaca de
la Palma - American Victory
August 3, 1846 - Battle of Canoncito
- American Victory
August 18, 1846 - Battle of Santa Fe
- American Victory
September 21-24, 1846
- Battle of Monterrey - American Victory
September 22-30, 1846
- Siege of Los Angeles - Mexican Victory
September 26-27, 1846
- Battle of Chino - Mexican Victory
October 7, 1846 - Battle of Dominguez
Rancho - Mexican Victory
December 6, 1846 - Battle of San Pasqual
- Mexican Victory
January 2, 1847 - Battle of Santa Clara
- American Victory
January 8, 1847 - Battle of Rio San
Gabriel - American Victory
January 9, 1847 - Battle of La Mesa
- American Victory
January 29, 1847 - Battle of Embudo Pass
- American Victory
February 22-23, 1847
- Battle of Buena Vista - American Victory
February 28, 1847 - Battle of the
Sacramento - American Victory
March 9-29, 1847 - Siege of Veracruz
- American Victory
April 17-18, 1847 - Battle of Cerro Gordo
- American Victory
July 6, 1847 - Battle of Las Vegas
- American Victory
August 20, 1847 - Battle of Contreras
- American Victory
August 20, 1847 - Battle of Churubusco
- American Victory
September 8, 1847 - Battle of Molino del
Rey - American Victory
September 12-13, 1847
- Battle of Chapultepec - American Victory
September 13-15, 1847
- Battle for Mexico
City - American Victory
October
2, 1847 - Battle of Mulege - Mexican Victory
October 12, 1847 -
Siege of Puebla - American Victory
October 31, 1847 -
Bombardment of Guaymas - American Victory
November 16/17, 1847
- Battle of La Paz - American Victory
November 20/21, 1847
- Battle of San Jose del Cabo - American Victory
November 27-December
8, 1847 - Siege of La Paz - American Victory
Dates of Battles -
Names of Battles - Results of Battles
Mexican American War
for kids: US and Mexico
For additional facts and information
about the history of the US and Mexico refer to
US and the Mexican Revolution.
Mexican American War for kids - President James K
Polk Video
The article on the
Mexican American War provides an overview of one of the Important
issues of his presidential term in office. The following James K
Polk video will give you additional important facts and dates about
the political events experienced by the 11th American President
whose presidency spanned from March 4, 1845 to March 4, 1849.
Mexican American War
● Facts and
James K Polk history timeline for
kids and schools
●
Definition of the Mexican American
War in US history
●
Facts about the Mexican American War
●
James K Polk Presidency from March
4, 1845 to March 4, 1849
●
Fast, fun, Mexican American War
about Important events in his
presidency
●
Foreign & Domestic policies of
President James K Polk
●
James K Polk Presidency and the
Mexican American War for schools,
homework, kids and children
|