|
The Cold War
Map:
Iron Curtain border
|
The
Cold War Facts: Fast Fact Sheet (1945 - 1991)
Fast, fun facts and Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ's)
about the Cold War.
What was the Cold War? The Cold War
(1945 - 1991) was the name given to the
tense relationship and "non-hostile
belligerency" between the United States and
its
NATO allies, and the Soviet Union and
its allies in the
Warsaw Pact
Why was it called the Cold War? The Cold
War was so called because of the icy
relationship between the USSR and USA
starting at the end of WW2. Because two
great powers never directly fought each
other it was called a "cold war", meaning
there was no physical fighting and described
as "non-hostile belligerency". It
was a "War of Words".
When did the Cold War start?
The Cold War started in 1945 at the end of
WW2 as the United States developed the first
Atomic Bomb and the power struggle between
the USA and the USSR began.
When did the Cold War end?
The Cold War ended after a period of 46
years when the Soviet Union fell in 1991
ending the Cold War.
The Cold War Facts
for kids:
What Caused the Cold War?
The origins and causes of the Cold War began at the
end of WW2 with the
Yalta
Conference and then the Potsdam
conference which was marked by the ideological differences
between Truman and Stalin. Increased Soviet power in Eastern Europe
with the eastern Bloc led to the descent of the Iron Curtain, the
border between the East and the West. America believed it should
contain Communism which led to the
Truman Doctrine and the
Marshall
Plan.
The Cold War Facts
for kids: How was the Cold War
Fought?
The Cold War was 'fought' with words, by spying
and entering a military arms competition. Vast amounts of money were
spent on defense and nuclear arms. The USA and the USSR competed to
produce new technological and industrial innovations which included
space exploration, satellites and the race to the moon.
The Cold War Facts
for kids: What Countries were
involved in the Cold War?
NATO Countries (The West)
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was the
military alliance of the West during the Cold War that was
established in 1949. The members of NATO were the United States, the
United Kingdom, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, France,
Canada, Portugal, Italy, Norway, Denmark and Iceland. Three years
later, on 18 February 1952, Greece and Turkey also joined.
The Cold War Facts
for kids:
The
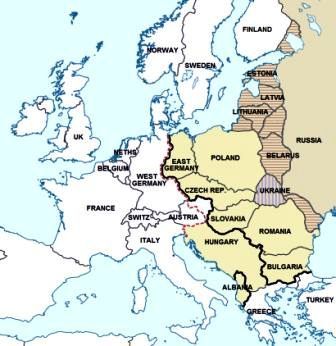
Warsaw Pact Countries (The East), the Iron Curtain
The Warsaw Pact (14 May 1955 - 1 July 1991) was
the USSR response to the NATO treaty at the start of the Cold War.
The
Warsaw Pact was a
defense treaty among eight communist 'satellite states' of Eastern
Europe dominated by the USSR during the Cold War. The members of the
Warsaw Pact were Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany,
Hungary, Poland, Romania and the Soviet Union. The countries were
referred to as the Eastern Bloc and their location was described as
being behind the "Iron Curtain", the boundary that separated the free democratic
countries of the West with the communist dominated
countries of the East, as shown in the map.
The Cold War Facts
for kids:
Key People - The Cold War Presidents
The Key people during the Cold War were the leaders of
the USA and the USSR. There were nine Cold War Presidents between
1945 - 1991. The names of the Cold War Presidents were Harry Truman,
Dwight D Eisenhower, John F Kennedy, Lyndon B Johnson, Richard
Nixon, Gerald Ford, Jimmy Carter, Ronald Reagan and George H Bush.
The Cold War Facts
for kids:
Key People - The Soviet Leaders
The main Soviet Leaders during the Cold War were
Joseph Stalin who was Dictator of the Soviet Union from 3 April 1922
– 16 October 1952. Nikita Khrushchev who came to power in 1953 after
the death of Stalin. Khrushchev was in power until 1964, when
Leonid Brezhnev had him ousted. Leonid Brezhnev was the leader of
the USSR for 18 years from 14 October 1964 – 10 November 1982. Two
short-lived leaders emerged. Yuri Andropov ruled the USSR from 12
November 1982 – 9 February 1984 followed by Konstantin Chernenko who
was in office from 13 February 1984 – 10 March 1985. Mikhail
Gorbachev led from 15 March, 1990 – 25 December, 1991 and
introduced the policies of Glasnost and Perestroika which
contributed to the fall of the Iron Curtain and the Soviet
Union.
The Cold
War Facts
for kids: Cold War Arms
Race
Summary and Definition: The
Cold War Arms Race between
the US and the USSR began following the development of the Atomic
Bomb and terrified the whole world with the threat of nuclear
annihilation.
The Cold
War Facts
for kids: Cold War Space Race
Summary and Definition: The
Cold War Space Race (1957
- 1975) was a competition in the exploration of space between the
United States and the Soviet Union.
The Cold
War Facts
for kids:
Capitalism vs Communism Economic Systems
Summary and Definition: Capitalism was the economic
system of the West based on private ownership (rather than
government ownership) and the free market system. Communism
encompassed the economic system of the East based on government
ownership and the control of resources.
The Cold War Facts
for kids:
The Red Scare
The
First
Red Scare was sparked by fear and suspicion of Russia and
Communism following the Russian Revolution (1918-1919). The Second
Red Scare erupted following WW2 with anti-communist hysteria in the
United States sparked by fears of the Cold War Nuclear Arms Race and
communist spies.
The Cold
War Facts
for kids: Cold War Brinkmanship
Summary and Definition: Brinkmanship is a term coined
during the Cold War to describe the tactic of reaching the brink or
verge of conflict without actually getting into a war. Cold War
Brinkmanship was advocated by John Foster Dulles the U.S. Secretary
of State from 1953-1959. The strategy of Cold War Brinkmanship
involved aggressive and risky measures seemingly to approach the
brink of war in order to persuade the opposition to retreat.
The Cold
War Facts
for kids: Cold War Propaganda
Summary and Definition: The Cold War era in America
was a period of high tension, mistrust and paranoia. Anti-communism
hysteria swept the nation as Americans feared the growth of
communism and witnessed the USSR and communists suppressing freedom
of speech, religion and civil rights and the oppression or
resistance of its people. The Arms Race between the two nations saw
the ever increasing competition to develop more and more nuclear
weapons and the threat of a nuclear war. Terrified Americans felt
helpless as the Space race supplied means of a constant spy system
monitoring the USA ever 2 hours. Cold War Propaganda spread
Anti-USSR and Anti-Communist information in the many different forms
such as newspapers, posters, magazines, kid’s comic books,
literature, movies, television, radio, photographs and speeches.
Cold War propaganda shaped public opinion to ensure the support of
government policies and the massive spending required to compete
with the Soviets.
The Cold
War Facts
for kids: Cold War Espionage
Summary and Definition: The Cold War involved the
world of Espionage as the East and the West attempted to
obtain the secrets of their Cold War opponents. Cold War espionage
involved activities aimed at the gathering of Intelligence during
the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union. The CIA
in the USA and the KGB in the USSR became synonymous with Cold War
espionage. The KGB ‘Committee for State Security’ was formed in 1954
as the Soviet's intelligence-gathering and espionage agency and
secret police. The Stasi, the East German secret police agency was
one of the most repressive and brutal security forces of the Cold
War. The CIA was formed in 1947 and involved in the surveillance of
suspected foreign agents, covert operations and the deployment of
agents abroad. The National Security Agency (NSA) obtained secret
information by intercepting, monitoring, and decoding signals and
radio traffic. The Federal Bureau of Investigations (FBI) was
responsible for investigating domestic issues such as espionage and
treasonable activities. Berlin was referred to as 'Spy Central'. The
Berlin Tunnel was a highly elaborate secret passage that US and
British agents used to gather information on KGB communication.
Spies played an important role in espionage as did Cold War
technology. Spy planes were introduced and the US Corona missions
(camera-carrying satellites) and the Zenit Spy Satellite developed
by the USSR.
The Cold
War Facts
for kids: Cold War Spies
Summary and Definition: The Cold War spies played an
important role in espionage and covert operations. Spies gathered
information in many ways, including including intercepting
communications, stealing documents, setting up ‘bugs’ (listening
devices) or other means of surveillance, sabotage operations, paying
informers and using double-agents. The most famous US nuclear spies
were Julius and Ethel Rosenberg. Julius and Ethel Rosenberg were
charged with heading a Soviet spy ring and were condemned to death
for espionage.
Alger Hiss, Elizabeth Bentley, and Whittaker Chambers
were other famous spies of the Cold War era. American CIA analyst
Aldrich Ames was one of the most successful Soviet double agents of
the Cold War. The British ‘Cambridge Five’ including Guy Burgess,
Donald Maclean and Kim Philby passed over thousands of confidential
documents to the USSR.
The Cold War Facts
for kids:
Strategies and Doctrines
The Cold War lasted for 46 years from 1945 - 1991.
Many of the Key events of the Cold War occurred over several years
such as the Cold War Arms Race and the Cold War Space Race. Various
strategies and doctrines were also a feature of the Cold War
although not related to specific events. These include the Detente,
Raprochement, Glasnost, Perestroika, Mutually Assured Destruction (MAD), and the Domino Theory.
The Cold
War Facts
for kids: Detente
Summary and Definition:
Detente is a political term,
taken from the French word meaning release from tension and the
relaxation in a political situation. During the Cold War the term
Detente signified the state of improved relations and an easing of
tensions between the East and the West and a temporary ‘thaw’ in
US-Soviet relations. The first signs of detente followed the
Cuban Missile Crisis when in August 1963 the USSR, the United States
and Great Britain signed the first Nuclear Test Ban treaty. Detente
declined during the late 1970's due to the active support of the
USSR of Communist revolutionary movements in the Third World
contributing to a revival of the Cold War.
The Cold
War Facts
for kids: Rapprochement
The term rapprochement derives
from the French word describing the reconciliation or
re-establishment of cordial relations between previously nations
that were previously hostile. In the context of the Cold War, the
term 'rapprochement' refers to the improved relations that occurred
during detente during the early 1970s and the Gorbachev era during
the late 1980s.
The Cold
War Facts
for kids: Glasnost and
Perestroika
Summary and Definition:
Glasnost and Perestroika are
Russian words closely associated with the late stages that led to
the end of the Cold War. Perestroika and Glasnost were terms that
encompassed many reform measures in the Soviet Union and the
democratization of the Communist Party. Perestroika and Glasnost
were promoted through the policies of Mikhail Gorbachev. The term
'Glasnost' is the Russian word meaning ‘openness’ especially in
relation to public scrutiny. 'Glasnost' encompassed Soviet reforms
implemented by Mikhail Gorbachev during the late 1980s, that
encouraged open debate and freedom of speech. Mikhail Gorbachev gave
great emphasis to 'Glasnost' in his speech of March 11, 1985. The
term 'Perestroika' is the Russian word meaning "reform, rebuilding,
reconstruction" used in relation to changes in Soviet society and
the economic policy allowing competition in business.
The Cold
War Facts
for kids: The Domino Theory
Summary and Definition: The
US Policy of Containment led to the
Domino Theory which related to
the spread of communist rule during the Cold War. The theory
speculated that if one region came under the influence of communism,
then the surrounding countries would follow in a falling domino
effect. U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower put the theory
into words, although he never directly used the term "domino
theory", when referring to communism in Indochina during a news
conference on April 7, 1954.
The Cold War Facts
for kids:
The
Main Events
During this period in history there were nine Cold War Presidents. The main
events of the Cold War that were related to specific dates included the
Bay of Pigs Invasion, the
Cuban Missile Crisis, the
Berlin Blockade and the
Berlin Airlift, the
Soviet Invasion of Hungary and the Hungarian Revolution, the
Korean
War, the
Vietnam War, the
U2 incident and the
Fall of the Berlin Wall.
The Cold War Facts
for kids:
Summaries
and Definitions of the Main Events
Summaries and definitions of the Main Events and defining moments
during the Cold War are summarized below providing a fast overview
of this dangerous time in history that brought the world to the
brink of a Nuclear War.
Cold War Events (1945 - 1947) Yalta Conference
● Potsdam Conference ● The United Nations
● The Iron Curtain ● The Long Telegram
● Operation
Crossroads ● Containment ● The Truman
Doctrine ● The Marshall Plan ● National Security
Act of 1947 ●
Cold War Events (1948 - 1955) Founding of West Germany
● NATO ● Berlin Airlift ● Berlin Blockade
● McCarthyism and HUAC ● CONELRAD ● Mao Zedong
● The Korean War ● The Vietnam
War ●
Cold War Events (1956 - 1961) Bay of Pigs Invasion
● Cuban Missile Crisis ● U-2 Incident
● Berlin Wall built ● Secret Speech ● Hungarian Revolution
●
Checkpoint Charlie Incident ●
Cold War Events (1968 - 1991) Prague Spring
● SALT Agreements ● Soviet Invasion of
Afghanistan ● Star Wars ● Fall of the Berlin
Wall ● Collapse of the Soviet
Union ● End of
the Cold War ●
The Cold
War Facts
for kids: Cold War Movies
Summary and Definition: The most famous Cold War
Movies include Red Dawn (1984 movie), Fail-Safe (1964) The Spy Who
Came in from the Cold (1965), The Ipcress File (1965), The Hunt for
Red October (1990 movie), The Manchurian Candidate (1962), A
Gathering of Eagles (1963), The Third Man (1949 movie), The Bedford
Incident (1965), The Spy Who Came in from the Cold (1965), Thirteen
Days (2000), Rocky IV (1985) and Tinker Tailor Soldier Spy (2011
movie). Watching these Cold War movies provides a good insight into
the tensions and events during this important time in history.
Cold War Facts and
Timeline for kids
●
Interesting Facts and Cold War timeline for kids and schools
●
Summary and Definition of the Cold War in US history
●
Facts and timeline with important dates and key
events
● Timeline with important dates and key
events
●
Fast, fun, interesting
facts and timeline
●
Foreign & Domestic
policy of American Presidents
● Cold War facts for schools,
homework, kids and children |