|
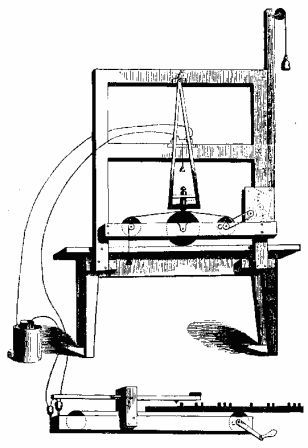
Morse
Electric Telegraph Machine and Key
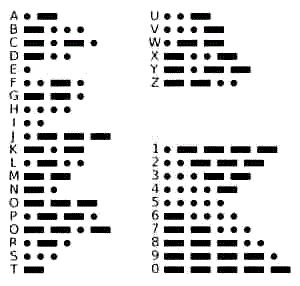
The Morse Code
|
The First Telegraph and
Samuel Morse
The telegraph is an electromagnet connected to a battery
via a switch. A telegraph system transmits signals by
using an electrical device that consists of a machine to
send signals by a wire to a receiving machine. The
signals are sent by a code to represent the alphabet and
numbers.
The First Telegraph: The
Problem
The problem with the electric telegraph was that an
electric current could be arranged in only two ways. The
electric current is either flowing and it is “On,” or
the current is not flowing and it is "Off". Samuel Morse
found a way to use the flow of electric current to make
a code that could be sent along the wires.
The First Telegraph:
The Morse Key
Samuel Morse discovered that if a man at
one end of a line of wire pressed down a key (the
sender), electricity could be made at the same moment to
automatically press down another key at the other end of
the line of wire and marked by the receiving machine on
a moving strip of paper. He invented the Morse Key that
could create short and long bursts of electric current
(called pulses) using long or short taps on the Morse
key machine.
The First Telegraph:
Messages
Samuel Morse discovered that the receiving
machine at the farther end of the line could be so
arranged as to make an impression on a piece of paper
that was slowly drawn under it by clockwork. He then had
to work out a way that the impression could convey a
message - he succeeded and this invention would be
called the Morse Code.
First Telegraph: The Morse Code
Samuel Morse and his assistant,
Alfred Vail, realized that if the man at one end of the
line held his key down for only an instant, this
impression would look like a dot. If the man held it
down longer, it would look like a short dash. Samuel
Morse combined these dots and dashes into an alphabet -
see the picture of the Morse Code on your left.
By
combining dots and dashes to represent letters in the
alphabet it became possible to send messages from a
sender to a receiver using the Morse Code. The next
stage was to simply add more codes using dots and dashes
to represent numbers. The Morse Code was complete.
Samuel Morse used an electromagnet to move a pencil and
mark a moving strip of paper with short and long marks
depending on whether the key was held closed for a short
time (dots) or a long time (dashes)
First Telegraph: How the electric telegraph worked
The Morse
telegraph system was basically an electrical circuit consisting of 3
parts all linked together by a wire. The battery supplied the
voltage, the Morse Key completed, or broke, the electric circuit and
the electromagnet for the 'sounder'.
First Telegraph: The First Message is sent in 1838
The first telegram in the United States was sent by Samuel Morse on
11 January 1838, across two miles (3 km) of wire at Speedwell
Ironworks near Morristown, New Jersey. The message read "A patient
waiter is no loser." The Speedwell Iron Works was owned by
Alfred Vail's father who had given financial backing to the
inventors.
First Telegraph: Congress
Samuel Morse demonstrated his
telegraph system to a somewhat skeptical Congress. He sent telegraph
messages between the Senate and House and finally in 1843 he managed
to convince Congress to fund $10,000 for the construction of the
first telegraph line in the United States. The first telegraph line
ran for 30 miles from Washington, D.C., to Baltimore, Maryland.
First Telegraph: The Railroad Morse Code and the Telegraph Poles
The Morse
Code is also referred to as the Railroad Morse. His
'land-line' telegraphic communication system carried signals across
the land by lines (wires) supported by telegraph poles. The
land-line telegraph system used "sounders" to allow the receiving
operator to "hear" the clicking sounds of the Morse code and to
translate them into letters. Telegraph poles were erected alongside
the railroad from Washington to Baltimore. This made perfect sense
as the route had already been cleared due to the construction of the
railroad and it was easy to set up poles to carry the telegraph
wires. It is fortunate that the development of the telegraph
coincided with the establishment of the American railroads - refer
to
Railroads in
the 1800s for facts and information. Provisions in the Pacific
Railroad Acts were made for the telegraph companies, who had just
completed the First Transcontinental Telegraph in 1861, to combine
their lines with the telegraph lines of the
Transcontinental Railroad
as they were built.
First Telegraph: "What hath God wrought"
Following the construction of the first long distance telegraph line
Samuel Morse installed a telegraph key in the Supreme Court chamber
and invited members of Congress to witness the event. A young woman
called Annie
Ellsworth provided the first message
to be sent. The famous message was "What hath God wrought"
and were taken from the Bible (Numbers 23:23). Annie Ellsworth's
father was Henry Leavitt Ellsworth, the U.S. Patent Commissioner,
who had championed Samuel Morse’s invention and helped secure
funding for it. The first message was
sent by Samuel Morse in Washington on May 24, 1844 to Alfred Vail at
the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad "outer depot" in Baltimore,
Maryland.
Alfred Vail in Baltimore then asked: "What is the news from
Washington?" Samuel Morse then telegraphed political news from the
capital which were published as telegraphic dispatches in Baltimore
newspapers.
First Telegraph: Significance
The invention of the telegraph was one of the most
significant events in the history of the United
States and revolutionized communication throughout
the world. The Morse Code enabled messages to be
communicated at the rate of ten words every minute.
● The
Pony Express
ended with the completion of the
Transcontinental Telegraph in 1861
● Telegraph
wires ran through most of the settled areas of
the United States by the 1850's
● It allowed
people to communicate instantly over distances
that once required days or weeks of travel
● The telegraph
carried messages of news events and business
transactions
● The first
trans-Atlantic telegraph cable was installed in
1866
● The telegraph
was the precursor of today's complex wireless
communications systems including the telephone,
radio, television, FAX and the internet
●
The Civil War heralded the use of
portable telegraph units.
- refer to Civil War Inventions
and Technology
First Telegraph for
kids
The info about
the First Telegraph provides interesting facts and important
information about this important event that occured during the
presidency of the 8th President of the USA and this great
accomplishment helped to lead in the belief in the
Manifest Destiny of the United
States...
First Telegraph for kids - President Martin Van Buren Video
The article on the
First Telegraph provides an overview of one of the Important
events of his presidential term in office. For
additional info refer to
Facts on Industrial Revolution Inventions. The following
Martin Van Buren video will
give you additional important facts and dates about the political events experienced by the 8th American President whose presidency spanned from March 4, 1837 to March 4, 1841.
First Telegraph
●
Interesting Facts about
First Telegraph for kids and schools
●
Facts, causes and significance of the First Telegraph
●
The First Telegraph, a Important
event in US history
●
Martin Van Buren Presidency and the First Telegraph
●
Fast, fun, interesting facts about the First Telegraph
●
Foreign & Domestic
policies of President Martin Van Buren
● Martin Van Buren Presidency and
First Telegraph for schools,
homework, kids and children
|