|
Indian
Territory Map
|
1887
Dawes Act
The 1887 Dawes Act was
entitled an "Act to Provide for the Allotment of Lands
in Severalty to Indians on the Various Reservations".
1887
Dawes Act: Severalty
The word "severalty" meant that the ownership of land in
reservations would no longer be tribal or common, but
would belong to an individual.
1887
Dawes Act Purpose
The purpose
of the Dawes Act was ostensibly enacted to protect
Native American property rights and welfare during the
land rush that was anticipated when lands in Indian
Territory were opened for white settlement (1889
Oklahoma Land Rush). However, the purpose of the Dawes Severalty Act
was also an attempt to integrate Native American Indians
into white society by changing their nomadic lifestyle
to the static, settled western lifestyle of farmers and
settlers.
1887
Dawes Act for kids: Background History
The Indian Policy of the United States
government centered on the policy of allotment by which communally
held Native Indian tribal lands were divided into individually owned
private property. Native Indian lands were seized for settlement by
non-Indians and for development by railroads. The
1830 Indian Removal Act had given the federal government the
power to force the relocation of Native Indians, living in the east
of the country, to territory that was west of the Mississippi River,
referred to as Indian Territory, which had resulted in the horrific
re-location of the Five Civilized tribes along the infamous Trail of
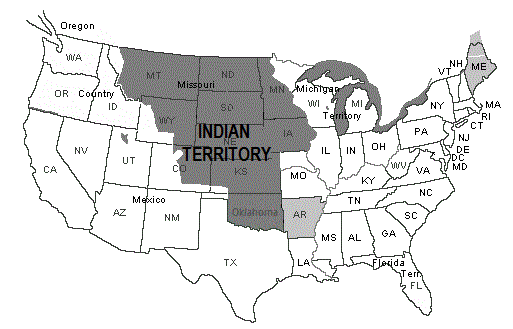
Tears. Congress had created a massive Indian Territory, from Texas
to the middle of the Missouri River as can be seen on the above
Indian Territory map and about 90,000 Native American Indians had
been forcibly relocated and obliged to merge with other tribes.
Purpose
of the
Dawes Act for kids: Henry L. Dawes
The Dawes Act was sponsored by lawyer
and U.S. Senator Henry L. Dawes of Massachusetts and was passed on
February 8, 1887. Henry Dawes also believed that the ownership of
land played an important part in persuading people to accept the
laws of the federal government. Dawes therefore suggested that
Native Americans should be granted land in exchange for renouncing
tribal allegiances. Senator Henry Dawes might have been well
intentioned but he clearly favored the assimilation of the Native
American Indian. Henry Dawes expressed his belief in the
civilizing power of owning land and property was quoted as saying
that that to be civilized was:
"...to wear civilized clothes...cultivate the ground, live in
houses, ride in Studebaker wagons,
send children to school, drink whiskey [and] own property."
The
Purpose of the
Dawes Act for kids
The purpose of the Dawes Act were as
follows:
Purpose of the Dawes Act: To break up tribes
Purpose of the Dawes Act: To halt the nomadic
lifestyle of Native American Indians
Purpose of the Dawes Act: To integrate Native
Indians into the lifestyle and culture of western
Americans
Purpose of the Dawes Act: To enroll with the
Bureau of Indian Affairs - later called the 'Dawes
Rolls'
Purpose of the Dawes Act: To encourage Native
Indians to adopt a settled farming based existence
Purpose of the Dawes Act: To reduce the cost of
the administration of Native American Indians
Purpose of the Dawes Act: To settle and allot
individual Native Indians plots of land
Purpose of the Dawes Act: To open the remainder
of the 'surplus' land to white settlers for profit
1887
Dawes Act for kids
The info about the Dawes Act provides interesting facts and
important information about this important event that occured during the presidency of the 22nd and 24th President of the United States of America.
Provisions of the Dawes Act for kids
The provisions of the Dawes Act were
as follows:
Provisions of the Act:
Native Americans
registering on a tribal "roll" were
granted allotments of reservation land
Provisions of the Act:
To provide for the
granting of landholdings to individual
Native Americans, replacing communal
tribal holdings:
● 160 acres if
they are to farm
● 80 acres if
they are to raise cattle
● 40 acres for
any normal living purposes
Provisions of the Act:
Each Native American
Indian will choose his or her own
allotment and the family will choose a
land allotment for each minor child.
Provisions of the Act:
The U.S. agent to
certify each allotment and provide two
copies of the certification to the
Commissioner of Indian Affairs
Provisions of the Act:
Native Americans not
residing on their reservation, or
without reservations, will receive an
equal land allotment
Provisions of the Act:
A Secretary of the
Interior will hold the allotments "in
trust" for 25 years
Provisions of the Act:
On completion of the
land patent process, the allotment
holder will become a United States
citizen
Provisions of the Act:
The Five Civilized
Tribes and several other tribes were
exempt from the act
1887
Dawes Act: Why did the Dawes Act fail?
The Dawes Act failed because the plots
were too small for sustainable agriculture. The
Native American Indians lacked tools, money,
experience or expertise in farming. The farming
lifestyle was a completely alien way of life. The
Bureau of Indian Affairs failed to manage the
process fairly or efficiently. Another reason why
the Dawes Act failed was because Native Indians were
suspicious of the federal government and appalled by
previous relocation efforts. The Native American
Indians who had refused to submit to previous
relocations refused to register on the Dawes Rolls
for fear that they would be caught and punished.
Effect and Significance
of the
Dawes Act
The effect and significance of the
Dawes Act was that
● In 1889,
the “Unassigned Lands” in Indian Territory were
officially opened to white settlement
● Many
elements of Native American tribal culture
disappeared
● Whole
tribes of Native Indians disappeared
● The
reservation system was nearly destroyed
● Before the
Dawes Act, 150 million acres lands remained in
Indian hands - within 20 years, two-thirds of
their land was gone
1887
Dawes Act for kids: The Dawes Commission and the Dawes Rolls
The Dawes Act was amended in 1891 and
again in 1906 by the Burke Act. In 1893, Henry Dawes
was appointed to head a three-member commission (the
Dawes Commission) to the Five Civilized Tribes to
negotiate agreements with the leaders of the
Cherokee, Choctaw, Chickasaw, Creek, and Seminole
tribes that would end tribal land ownership and give
each member individual possession of a portion of
the tribal lands. The Dawes Rolls list individuals
who chose to enroll and were approved for membership
in the Five Civilized Tribes.
1887
Dawes Act for kids - President Grover Cleveland Video
The article on the
1887 Dawes Severalty Act provides detailed facts and a summary of one of the important events during his presidential term in office. The following
Grover Cleveland video will
give you additional important facts and dates about the political events experienced by the 22nd and 24th President of the
United States whose presidencies spanned from March 4, 1885 to March 4, 1889
and from March 4, 1893 - March 4,1897.
1887 Dawes Act
●
Interesting Facts about Dawes Act for kids and schools
●
Summary of the Dawes Act in US history
●
The Dawes Severalty Act, a major
event in US history
●
Grover Cleveland history timeline
of major events
●
Fast, Dawes Act
about major events in his presidency
●
Foreign & Domestic
policies of President Grover Cleveland
●
Grover Cleveland Presidency and
Dawes Severalty Act for schools,
homework, kids and children |